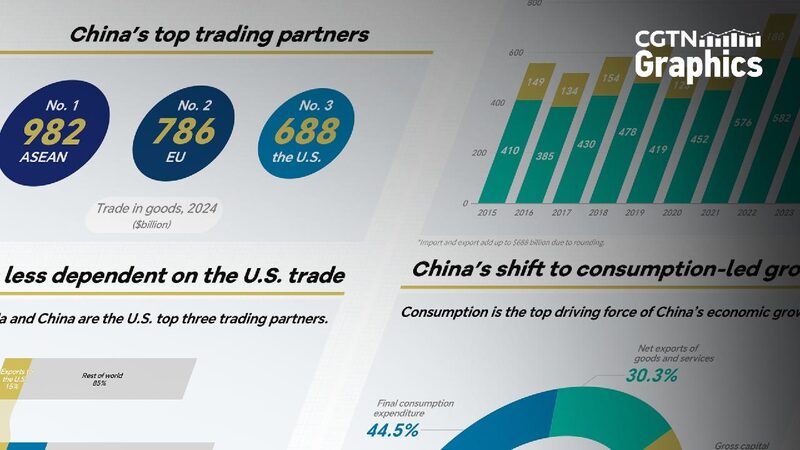
China is steadily reducing its reliance on trade with the United States, focusing instead on strengthening partnerships with other global players. According to recent reports, the Chinese mainland has increased trade with the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and the European Union (EU), with the U.S. dropping in rank among its trading partners.
This shift has seen the U.S. fall to third place among China’s trading partners. Trade with ASEAN has surged, followed by significant growth with the EU. Exports to the U.S. now account for a smaller percentage of China’s total exports, highlighting a changing landscape in global trade dynamics.
China is also focusing on boosting domestic consumption to drive economic growth. By expanding domestic demand, consumption has become the top driving force of the country’s economic expansion. In recent years, consumption has significantly contributed to the Chinese mainland’s overall GDP growth.
This move towards diversifying trade partnerships and enhancing domestic consumption reflects China’s aim to build a more resilient economy. For young people in the Global South, this shift could open up new opportunities for collaboration and economic growth in their own regions.
Reference(s):
cgtn.com