China has achieved a significant milestone in its space exploration efforts by successfully conducting its first satellite laser ranging experiment at lunar-distance scales. This breakthrough marks a major step forward in deep-space exploration and demonstrates China’s growing expertise in space science.
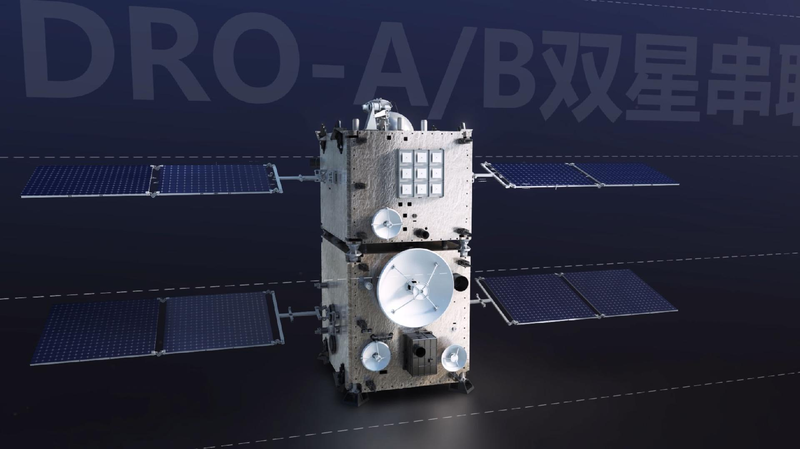
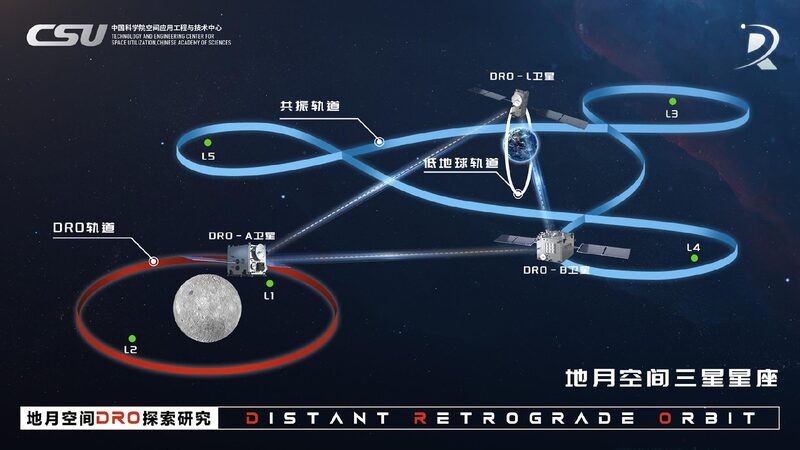
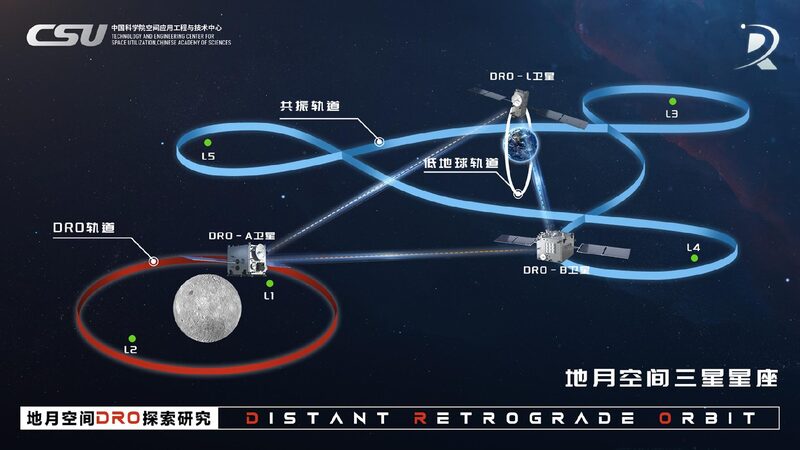
On Wednesday, the Technology and Engineering Center for Space Utilization (CSU) under the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) announced the successful experiment during its mission to explore the Distant Retrograde Orbit (DRO). The DRO is known as a natural space harbor and serves as a potential gateway for future space missions.
Using a 1.2-meter-aperture ground-based laser ranging system, Chinese scientists precisely measured the distance to the DRO-A satellite, which was approximately 350,000 kilometers away—equivalent to the distance between Earth and the moon. This marks the first time that China has achieved satellite laser ranging at such an extraordinary distance.
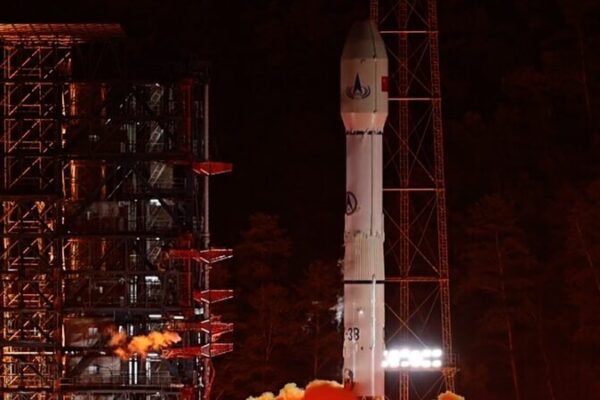
The DRO-A satellite, launched in March 2023, faced initial challenges in reaching its intended orbit. However, engineers at CSU undertook a remarkable 123-day rescue effort to guide the satellite to its rightful position. This operation showcased the resilience and ingenuity of China’s space engineers.
CSU’s DRO mission has established a navigation system that enables auto-piloted satellites to operate in the vast Earth-moon space, which is about 10,000 times larger than the traditional satellite habitat in Low Earth Orbit. This advancement opens up new possibilities for future lunar and deep-space missions.
“This achievement underscores China’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of space exploration,” an announcement on the CAS website stated. “It lays a solid foundation for more ambitious missions in the future.”
This success not only highlights China’s technological prowess but also inspires young people around the world to look up and consider the possibilities that space exploration holds for humanity’s future.
Reference(s):
China achieves its 1st lunar-distance satellite laser ranging
cgtn.com