
China Enacts First Energy Law, Paving Way for Green Future
China’s first energy law takes effect, marking a crucial step towards energy security and a green, low-carbon future in line with global climate action.
News for people and friends

China’s first energy law takes effect, marking a crucial step towards energy security and a green, low-carbon future in line with global climate action.

China calls on developed nations to honor climate funding commitments made at COP29, emphasizing the need for $1 trillion annually to support developing countries in the global energy transition.
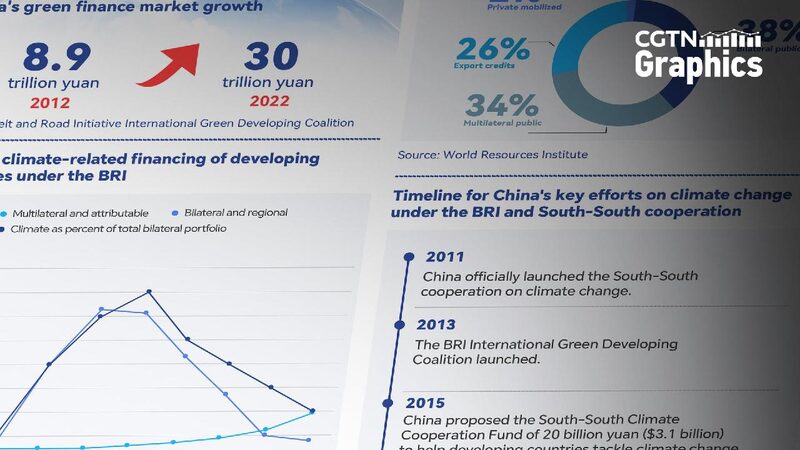
China is now a significant provider of global climate change funding, leading in renewable energy investments, especially in developing countries. Its efforts were highlighted at COP29 in Baku.

At COP29, China calls on nations to embrace ‘common but differentiated responsibilities’ to fight climate change, highlighting unity and adherence to the Paris Agreement.
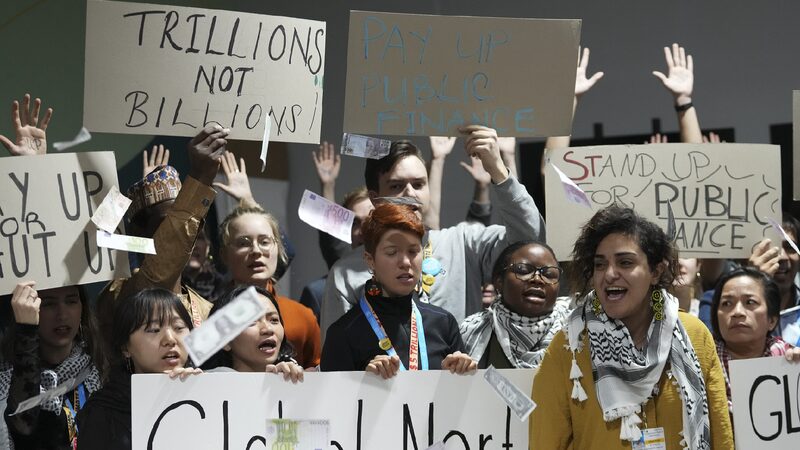
At COP29, developed nations agreed to provide $300 billion annually by 2035 to help developing countries tackle climate change. While it’s triple the previous commitment, many nations say it’s still far from enough.
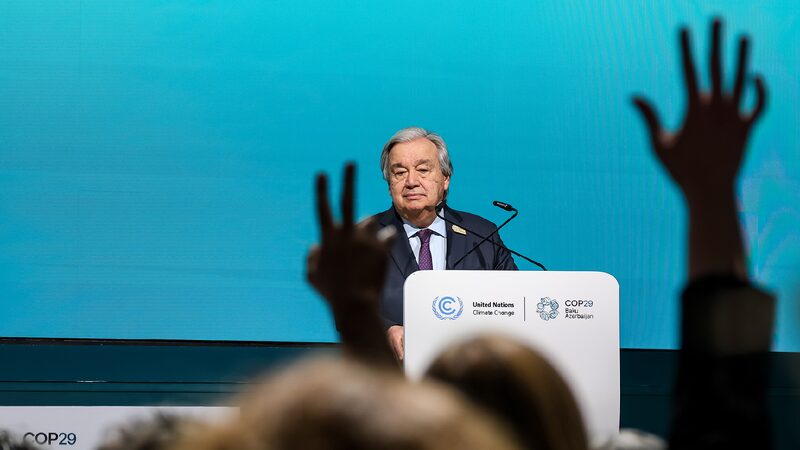

At COP29, climate negotiations stall as developing nations find proposed funding goals insufficient, leaving a daunting task ahead.

At COP29, leaders emphasized that tackling the climate crisis requires more than just money. Comprehensive strategies involving justice, technology, and cooperation are essential for real progress.

COP29 summit runs into overtime as leaders debate a $250 billion climate finance proposal, aiming to finalize agreements on funding and carbon markets to tackle climate change.

At COP29, the Global South leads in climate action, but wealthier nations’ unmet promises hinder global progress. Is it time for developed countries to step up?

As the COP29 deadline nears, nations are urgently seeking consensus on new climate funding to support developing countries, but divisions persist between developed and developing nations.